Embedded computing
 Using the Pi Pico with an L298N module to control a 12V motor (Jul 2025)
Using the Pi Pico with an L298N module to control a 12V motor (Jul 2025)The L298N is a convenient and inexpensive H-bridge motor controller, which interfaces nicely with the Pi Pico.
Categories: electronics, embedded computing, Pico
 Why using crude PWM for sampled audio output on the Raspberry Pi Pico doesn't sound that great (Jul 2025)
Why using crude PWM for sampled audio output on the Raspberry Pi Pico doesn't sound that great (Jul 2025)We can play sampled audio from a Pi Pico, using the built-in PWM controller, a single GPIO pin, and a handful of discrete electronic components. It's cheap and simple -- but how well does it work?
Categories: embedded computing, Pico
 Raspberry Pi Pico: loading code into RAM and running it -- part 1 (Jun 2025)
Raspberry Pi Pico: loading code into RAM and running it -- part 1 (Jun 2025)This is the first of (at least) two articles on loading and running arbitrary executable code into RAM on the Pico, and running it.
Categories: C, embedded computing, Pico
 Some thoughts on Pimoroni's Pico GFX Pack LCD module (Mar 2025)
Some thoughts on Pimoroni's Pico GFX Pack LCD module (Mar 2025)Pimoroni's 'GFX Pack' is an inexpensive, low-power LCD display, with modest resolution. This article describes my experience using and programming it.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, embedded computing, Pico
 ARM assembly-language programming for the Raspberry Pi (Feb 2025)
ARM assembly-language programming for the Raspberry Pi (Feb 2025)A series of simple, progressive examples that demonstrate the essential features of programming in ARM assembly language.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, software development, embedded computing, assembly
 C development for Linux without a standard library (Mar 2024)
C development for Linux without a standard library (Mar 2024)There are relatively few good reasons for writing C code without using a standard C library. However, doing so provides valuable insights into how compilers and operating systems work, and is worth doing if only for its educational value.
Categories: software development, C, embedded computing
 Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part one: booting to a root shell (Nov 2023)
Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part one: booting to a root shell (Nov 2023)This article is part of a series on building a custom Linux installation for a Raspberry Pi-based appliance. It explains how to make a bootable SD card with Pi firmware, a Linux kernel, and a shell. It's about as minimal as a Linux system can be.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, Linux, embedded computing
 Using flash memory as non-volatile storage on the Pi Pico microcontroller (Jun 2023)
Using flash memory as non-volatile storage on the Pi Pico microcontroller (Jun 2023)The Pi Pico is an impressive microcontroller for its size and cost, but it lacks specific non-volatile memory. This article explains how to use the program flash ROM for that purpose.
Categories: software development, C, Linux, embedded computing, Pico
 Why does my Raspberry Pi project keep displaying the 'lightning bolt' undervoltage indicator? (May 2023)
Why does my Raspberry Pi project keep displaying the 'lightning bolt' undervoltage indicator? (May 2023)The Raspberry Pi is widely used as part of a more complex electronic project or construction. There's a misconception that such a construction can be powered from the same cheap, nasty USB charger that is suitable to power a Pi on its own. Attempting to do this often leads to undervoltage situations. This article explains why, and what constructors can do about it.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, electronics, embedded computing
 Using media keys in a Linux console application (Mar 2023)
Using media keys in a Linux console application (Mar 2023)Mapping keyboard keys to key codes on Linux is well-documented for the graphical desktop. But what about console applications on embedded Linux systems? There's not much documentation in this area.
Categories: Linux, C, embedded computing
 Using the Linux framebuffer in C/C++ -- just the essentials (part 2) (Feb 2023)
Using the Linux framebuffer in C/C++ -- just the essentials (part 2) (Feb 2023)This article continues my original framebuffer just the essentials article, by describing how to handle less straightforward framebuffer configurations.
Categories: software development, C, Linux, embedded computing
 Using the Linux framebuffer in C/C++ -- just the essentials (Feb 2023)
Using the Linux framebuffer in C/C++ -- just the essentials (Feb 2023)The absolute minimum information needed to start using the Linux framebuffer as a graphical display in C/C++ applications.
Categories: software development, C, Linux, embedded computing
 pico-photo-clock: an easy-to-construct Pi Pico desktop photo clock (Jan 2023)
pico-photo-clock: an easy-to-construct Pi Pico desktop photo clock (Jan 2023)This article describes how to construct a desktop photo clock using a Raspberry Pi Pico and some solder-free peripherals.
Categories: embedded computing, Pico
 Using the Maxim DS3231 I2C real-time clock in C on the Raspberry Pi Pico (Jan 2023)
Using the Maxim DS3231 I2C real-time clock in C on the Raspberry Pi Pico (Jan 2023)The Maxim DS3231 I2C real-time clock is a reasonably accurate, inexpensive device, that is easy to interface to the Raspberry Pi Pico.
Categories: C, embedded computing, Pico
 Using ImageMagick to generate anti-aliased bitmap fonts for a microcontroller's LCD display (Jan 2023)
Using ImageMagick to generate anti-aliased bitmap fonts for a microcontroller's LCD display (Jan 2023)This article describes how to generate and use compressed, anti-aliased font data, for use in a microcontroller application.
Categories: C, Linux, embedded computing, Pico
 The Pi Pico, two years on (Jan 2023)
The Pi Pico, two years on (Jan 2023)I've been using the Raspberry Pi Pico for embedded projects for the last two years or so. What do I think of it now?
Categories: embedded computing, Pico
 Some thoughts on the Waveshare 3.5-inch LCD/SD module for the Raspberry Pi Pico (Jan 2023)
Some thoughts on the Waveshare 3.5-inch LCD/SD module for the Raspberry Pi Pico (Jan 2023)This is a versatile touchscreen display module with a strikingly low cost. But is it any good?
Categories: embedded computing, Pico
 Why 'int x = 0' is uninitialized data to the GNU C compiler (Jan 2023)
Why 'int x = 0' is uninitialized data to the GNU C compiler (Jan 2023)An oddity of the GCC C compiler that can lead to strange results, particularly in an embedded application
Categories: C, embedded computing
 Raspberry Pi Pico: loading code into RAM and running it -- part 2 (Dec 2022)
Raspberry Pi Pico: loading code into RAM and running it -- part 2 (Dec 2022)This is the second of (at least) two articles on loading and running arbitrary executable code into RAM on the Pico, and running it.
Categories: C, embedded computing, Pico
 Some thoughts on using a USB keyboard with the Raspberry Pi Pico (Nov 2022)
Some thoughts on using a USB keyboard with the Raspberry Pi Pico (Nov 2022)The Pi Pico has USB host support, and can work with a USB keyboard. Although there are some programming examples, the general approach to programming USB host operations is not well documented.
Categories: software development, C, embedded computing, Pico
 The costs and benefits of software pulse-width modulation on the Raspberry Pi (Sep 2022)
The costs and benefits of software pulse-width modulation on the Raspberry Pi (Sep 2022)The Raspberry Pi doesn't offer much in the way of analog outputs, or even hardware controlled PWM. Software-controlled PWM is an alternative in some applications, but it needs to be used carefully, if inefficiencies are to be avoided.
Categories: software development, C, embedded computing, Raspberry Pi
 Using an HD44780 LCD display module with the Raspberry Pi, from the ground up (Sep 2022)
Using an HD44780 LCD display module with the Raspberry Pi, from the ground up (Sep 2022)In this article I explain how to construct, and program in C, an I2C interface to the popular HD44780 LCD display for the Raspberry Pi. Between the article and the accompanying source code, no technical details are concealed: I present the complete hardware design and every line of C code needed to operate it.
Categories: software development, C, embedded computing, Raspberry Pi
 Monitoring an INA219 chip in a Raspberry Pi battery-backed power supply (Sep 2022)
Monitoring an INA219 chip in a Raspberry Pi battery-backed power supply (Sep 2022)Many battery-backed power supplies for the Raspberry Pi, and similar systems, use the INA219 current/voltage monitor IC. This device has an I2C interface by which the Pi can determine the battery voltage and current, and estimate the charge level and run-time. This article describes how to write C code that interacts with the INA219.
Categories: software development, C, embedded computing, Raspberry Pi
 Getting reasonably robust proximity measurements from an ultrasonic sensor on the Raspberry Pi (Sep 2022)
Getting reasonably robust proximity measurements from an ultrasonic sensor on the Raspberry Pi (Sep 2022)The HC-SR04 proximity sensor is an inexpensive and widely-used ultrasonic device. Connecting one to an HC-SR04 to a Raspberry Pi is a common educational exercise, but getting accurate, repeatable measurement of distance in a real application is actually quite difficult. This article explains why, and what can be done to improve matters.
Categories: software development, C, embedded computing, Raspberry Pi
 Using a shift register to control eight digital outputs with three GPIO lines on the Raspberry Pi (Sep 2022)
Using a shift register to control eight digital outputs with three GPIO lines on the Raspberry Pi (Sep 2022)A simple and inexpensive shift register can be used to increase the digital output provision of a Raspberry Pi or microcontroller. This well-know technique is easy to apply, but has some limitations that require careful consideration.
Categories: software development, C, embedded computing, Raspberry Pi
 Using the Qpid Proton C++ library to create a server for monitoring or telemetry data (May 2022)
Using the Qpid Proton C++ library to create a server for monitoring or telemetry data (May 2022)Collecting sensor data, or low-level system status information, is a job that is often best done in C/C++. Distributing this kind of data to other system components in a way that is platform- and language-independent can be a challenge. This article suggests a way to do this use AMQP message distribution.
Categories: embedded computing, middleware
 Raspberry Pi as a networked storage (NAS) device (Dec 2021)
Raspberry Pi as a networked storage (NAS) device (Dec 2021)How to construct a custom networked storage (NAS) unit based on a Raspberry Pi and two mirrored USB hard drives -- and why you might want to.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, embedded computing
 Making an 8x32 LED auxiliary display with a USB interface, from an LED matrix and a Raspberry Pi pico (Nov 2021)
Making an 8x32 LED auxiliary display with a USB interface, from an LED matrix and a Raspberry Pi pico (Nov 2021)A specific application of the Pico7219 library that I described in an earlier article.
Categories: embedded computing, Pico, electronics
 Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi (Sep 2021)
Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi (Sep 2021)Introducing a series of articles on building a custom Linux installation for the Raspberry Pi, for appliance applications.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, Linux, embedded computing
 Why you can sometimes connect 3.3V and 5V I2C devices (and probably shouldn't) (May 2021)
Why you can sometimes connect 3.3V and 5V I2C devices (and probably shouldn't) (May 2021)On websites, and in hobbyist kits for Raspberry Pi and Arduino, you'll often see I2C devices connected that have different supply voltages. This is (usually) safe and, in non-critical applications, tends to work. But why?
Categories: Raspberry Pi, electronics, embedded computing, Pico
 Controlling a chain of MAX7219 LED matrices using C on a Raspberry Pi Pico (May 2021)
Controlling a chain of MAX7219 LED matrices using C on a Raspberry Pi Pico (May 2021)The MAX7219 IC is widely used to control an 8x8 matrix of LED, but they can be chained to create much larger displays. This article describes how the chaining works, and how to create a driver for the Raspberry Pi Pico.
Categories: software development, C, embedded computing, Pico
 C-to-parallel IC (Apr 2021)
C-to-parallel IC (Apr 2021)Make an auxiliary LCD display for a computer that displays data sent to it over a USB connection. Ready-made devices of this sort are widely available, but it's more fun to build your own.
Categories: software development, C, Linux, embedded computing, Arduino
 Using an I2C analog-to-digital for temperature measurement on the Raspberry Pi (Apr 2021)
Using an I2C analog-to-digital for temperature measurement on the Raspberry Pi (Apr 2021)This article describes how to do simple temperature measurement with a Raspberry Pi, and I2C analog-to-digital converter, and a thermistor.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, electronics, embedded computing, C
 Building a custom mechanical keyboard from scratch (Feb 2021)
Building a custom mechanical keyboard from scratch (Feb 2021)There are many kits and plans available for constructing miniature mechanical keyboards. But what do you do if you want a layout the nobody else seems to use? Build it from scratch.
Categories: Arduino, embedded computing, C
 Reviving old keyboards for Arduino (Feb 2021)
Reviving old keyboards for Arduino (Feb 2021)Although connecting a USB keyboard to an Arduino-type microcontroller without addition hardware can be tricky, there are no such problems with many 90s keyboards. This article is about giving new life to old keyboards, by using them as input devices for microcontroller projects.
Categories: Arduino, embedded computing, retrocomputing
 Building and programming a USB keypad from the ground up (Jan 2021)
Building and programming a USB keypad from the ground up (Jan 2021)The first step towards designing and building a custom keyboard, from the very first principles, using an Arduino-type microcontroller.
Categories: Arduino, embedded computing, C
 Using Linux command-line tools for programming the SparkFun Pro Micro microcontroller (and similar) (Jan 2021)
Using Linux command-line tools for programming the SparkFun Pro Micro microcontroller (and similar) (Jan 2021)Although building and deploying a simple program to an Arduino board is a point-and-click operation using the Arduino IDE, implementing more complex programs requires more robust build tools. This article describes how to build on Linux using command-line tools -- a process that is nowhere near as easy as it should be. If we can build using command-line tools, we can manage a project using Makefiles and similar techniques.
Categories: Arduino, embedded computing, C
 A Raspberry Pi and touchscreen case that anybody can make (Jan 2021)
A Raspberry Pi and touchscreen case that anybody can make (Jan 2021)This is a design for a robust, wooden enclosure for a Raspberry Pi, battery power supply, and touchscreen, that can be made using hand tools.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, embedded computing, electronics
 Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part four: audio (Dec 2020)
Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part four: audio (Dec 2020)This article is part of a series on building a customer Linux installation for a Raspberry Pi-based appliance. It explains how to install and set up the minimum software to get audio playback working.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, Linux, embedded computing
 Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part three: services and remote access (Dec 2020)
Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part three: services and remote access (Dec 2020)This article is part of a series on building a customer Linux installation for a Raspberry Pi-based appliance. It explains how to set up a system which hitherto only boots to a root shell, to a network-aware installation with service management.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, Linux, embedded computing
 Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part two: early initialization (Dec 2020)
Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part two: early initialization (Dec 2020)This article is part of a series on building a customer Linux installation for a Raspberry Pi-based appliance. It explains how to obtain and install fundamental utilities for use in a system with a read-only filesystem, and no package manager.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, Linux, embedded computing
 Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part five: X (Dec 2020)
Rolling your own minimal embedded Linux for the Raspberry Pi -- part five: X (Dec 2020)It's entirely possible to run simple, X-based applications in an appliance-based Linux installation: you just have to dispense with the graphical desktop and all its baggage. This article explains how.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, Linux, embedded computing
 Switching a couple of amps with a Raspberry Pi and a relay (Dec 2020)
Switching a couple of amps with a Raspberry Pi and a relay (Dec 2020)Switching loads of an amp or two with a Raspberry Pi or a microcontroller can be accomplished using a small number of inexpensive components. Suitable circuits are widely published, but the details of operation are not always described.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, electronics, embedded computing
 Using an I2C analog-to-digital converter chip with the Raspberry Pi, from the ground up (Nov 2020)
Using an I2C analog-to-digital converter chip with the Raspberry Pi, from the ground up (Nov 2020)This article is about using an I2C analogue-to-digital device for applications like reading sensor values or monitoring backup batteries. With all the technical bits left in.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, electronics, embedded computing, C
 Using the FreeType library to render text nicely onto a Linux framebuffer (Nov 2020)
Using the FreeType library to render text nicely onto a Linux framebuffer (Nov 2020)Writing graphical applications for minimal and embedded Linux systems can present a challenge. One of the problems is producing nicely-rendered text without the facilities that a graphical desktop would provide. This article describes how to use the FreeType library to render text to the Linux framebuffer.
Categories: software development, C, Linux, embedded computing, Raspberry Pi
 Using the Raspberry Pi official 7-inch touch-screen in embedded applications (Jul 2020)
Using the Raspberry Pi official 7-inch touch-screen in embedded applications (Jul 2020)The official Raspberry Pi 7-inch touchscreen is a useful and well-designed piece of equipment but, if you're using it in a custom (hardware and/or software) build, you'll notice a lack of any relevant technical information. This article tries to supply some of that information.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, electronics, embedded computing
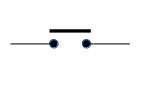 Handling GPIO-connected switches robustly in C on the Raspberry Pi (Jul 2020)
Handling GPIO-connected switches robustly in C on the Raspberry Pi (Jul 2020)It's surprisingly difficult to detect switch actuations in a robust way, dealing with contact bounce and other quirks. This article describes one approach to the problem in C.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, electronics, embedded computing
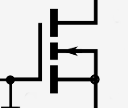 Why switching high currents using a MOSFET and a Raspberry Pi is not as straightforward as it looks (Jul 2020)
Why switching high currents using a MOSFET and a Raspberry Pi is not as straightforward as it looks (Jul 2020)Using a single MOSFET transistor for power switching in microcontroller applications is simple and low-cost, but it often doesn't work as well as expected. Either the switched device doesn't run at full capacity, or the MOSFET gets hot. This article explains why.
Categories: Raspberry Pi, electronics, embedded computing
 Extracting software from the Raspbian repository, for assembling a custom Linux image for the Raspberry Pi (Jul 2020)
Extracting software from the Raspbian repository, for assembling a custom Linux image for the Raspberry Pi (Jul 2020)Using the official Raspian repository to assist the construction of a custom Linux for embedded applications is quick and convenient, compared to building everything from source. However, this approach has certain hazards.
Categories: Linux, Raspberry Pi, embedded computing
Have you posted something in response to this page?
Feel free to send a webmention
to notify me, giving the URL of the blog or page that refers to
this one.